Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity, allowing them to collect and share data. IoT enables these “smart objects” to communicate with each other and with other internet-enabled devices, creating a vast network of interconnected devices that can exchange data and perform various tasks autonomously.
- Improved efficiency and productivity by automating and optimizing processes
- Generation of vast amounts of data for better-informed business decisions
- Enhanced customer experiences and new business models
- Reduced costs through improved asset management and supply chain visibility
Some common examples of IoT devices include:
- Smart home devices like thermostats and security systems
- Wearable technologies such as smartwatches and fitness trackers
- Personal medical devices for remote patient monitoring
- Autonomous vehicles with sensors mapping their surroundings.
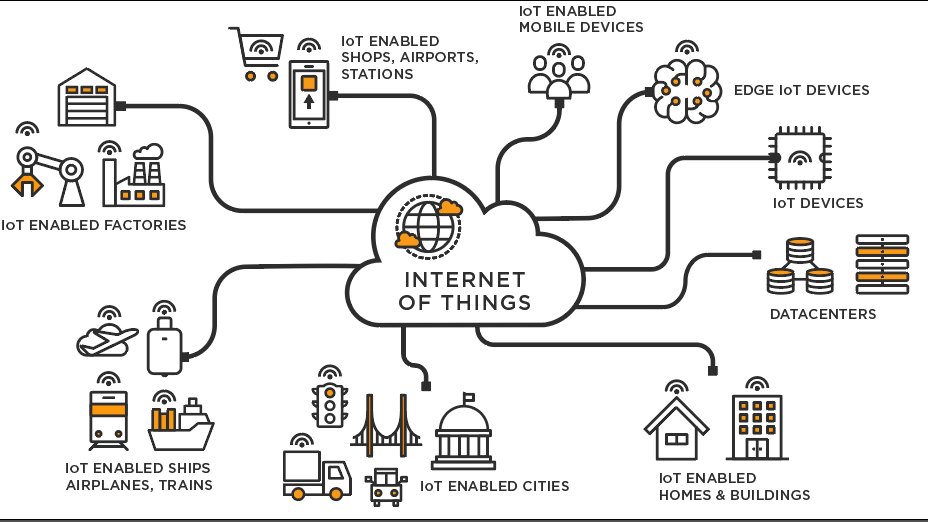
Key Benefits of IoT in Industry
- Real-Time Monitoring: IoT devices enable continuous monitoring of equipment and processes, allowing for immediate detection of anomalies and performance issues. This capability supports proactive maintenance and minimizes downtime, ultimately improving operational efficiency.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing data collected from sensors, companies can predict when equipment is likely to fail. This predictive approach allows for timely maintenance interventions, reducing unexpected breakdowns and extending the lifespan of machinery.
- Automation of Processes: IoT facilitates the automation of various industrial processes by enabling machines to communicate with each other. This interconnectedness leads to streamlined operations and enhanced productivity, as machines can adjust their functions based on real-time data.
- Improved Supply Chain Management: IoT enhances visibility throughout the supply chain by tracking materials and products in real-time. This capability allows for better inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics planning, leading to cost savings and improved service delivery.
- Data-Driven Insights: The integration of IoT allows for the collection and analysis of vast amounts of data, providing valuable insights into operational performance. Companies can leverage this data to optimize processes, improve product quality, and make informed business decisions.
- Enhanced Security: IoT systems can improve security by monitoring for unauthorized access and ensuring data integrity. Advanced security protocols can be implemented to protect sensitive information and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
- Energy Management: IoT technologies can monitor and optimize energy usage in industrial settings, helping companies reduce costs and minimize their environmental impact. Smart energy management systems can adjust consumption based on real-time demand.
Challenges in IoT Integration
While the benefits of IoT in industry are substantial, there are also challenges to consider:
- Interoperability: Integrating various IoT devices and systems can be complex due to the lack of uniform standards. Ensuring that different devices can communicate effectively is crucial for achieving seamless operations.
- Infrastructure Investment: Implementing IoT solutions often requires significant investment in infrastructure and training to ensure that staff can effectively utilize new technologies.
- Data Security: As IoT devices are connected to the internet, they are vulnerable to cyber threats. Ensuring robust security measures are in place is essential to protect sensitive data and maintain operational integrity.
Conclusion
The integration of IoT into industrial processes is revolutionizing how companies operate, driving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing decision-making capabilities. As industries continue to adopt IoT technologies, addressing the associated challenges will be critical to maximizing the benefits and ensuring long-term competitiveness.
key differences between IoT and traditional industrial automation
The key differences between the Internet of Things (IoT) and traditional industrial automation systems are:
Connectivity and Data Exchange
IoT enables seamless connectivity between a wide range of devices, sensors, and objects through the internet, facilitating real-time data exchange. Traditional industrial automation systems often relied on proprietary protocols and closed networks, limiting connectivity and data sharing capabilities.
Scalability and Flexibility
IoT solutions are designed to be scalable, allowing for easy integration of new devices and sensors as needs evolve. They provide greater flexibility in adapting to changing requirements. Traditional automation systems can be more rigid and challenging to scale or modify.
Data Analytics and Intelligence
IoT incorporates advanced data analytics capabilities, enabling intelligent decision-making based on the vast amounts of data collected from connected devices. This allows for optimized processes, predictive maintenance, and enhanced efficiency. Traditional systems may have more limited data analysis capabilities.
Interoperability and Integration
IoT emphasizes interoperability, allowing devices from different manufacturers to communicate and work together. This enables seamless integration across various systems and processes. Traditional automation systems often relied on proprietary technologies, making integration more challenging.
Security and Reliability
IoT solutions require robust security measures to protect against cyber threats and ensure data integrity. They prioritize reliability to minimize disruptions in industrial operations. Traditional automation systems may have had more limited security features and were designed for specific environments.
Scope and Applications
IoT has a broader scope, encompassing consumer, enterprise, and industrial applications. Industrial IoT (IIoT) focuses on specialized requirements of industrial settings, such as manufacturing, oil and gas, and utilities. Traditional automation systems were primarily designed for specific industrial applications. In summary, while both IoT and traditional industrial automation aim to enhance efficiency and productivity, IoT offers greater connectivity, flexibility, data analytics capabilities, and interoperability, enabling more advanced and adaptable industrial solutions.
FAQs about IoT in Industry
1. What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
Answer: The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices and objects embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to collect and exchange data over the internet. In industrial applications, IoT enhances monitoring, automation, and data analysis, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
2. How does IoT improve efficiency in industrial settings?
Answer: IoT improves efficiency by enabling real-time monitoring of equipment and processes, facilitating predictive maintenance, automating workflows, and enhancing supply chain management. By collecting and analyzing data, companies can optimize operations, reduce downtime, and make informed decisions.
3. What are some common applications of IoT in industry?
Answer: Common applications of IoT in industry include:
- Predictive maintenance of machinery
- Real-time inventory management
- Supply chain optimization
- Energy management and monitoring
- Quality control and assurance
- Smart manufacturing and automation
4. What are the benefits of implementing IoT in manufacturing?
Answer: The benefits of implementing IoT in manufacturing include:
- Increased operational efficiency and productivity
- Reduced downtime and maintenance costs
- Enhanced product quality and consistency
- Improved supply chain visibility and management
- Data-driven decision-making capabilities
- Greater flexibility and scalability in operations
5. What challenges are associated with IoT implementation in industry?
Answer: Challenges of IoT implementation include:
- Interoperability issues between different devices and systems
- Data security and privacy concerns
- High initial investment and infrastructure costs
- Complexity in managing and analyzing large volumes of data
- Need for skilled personnel to operate and maintain IoT systems.
Read Related Post
Social Media Influencers: Authentic Voices or Paid Actors?


