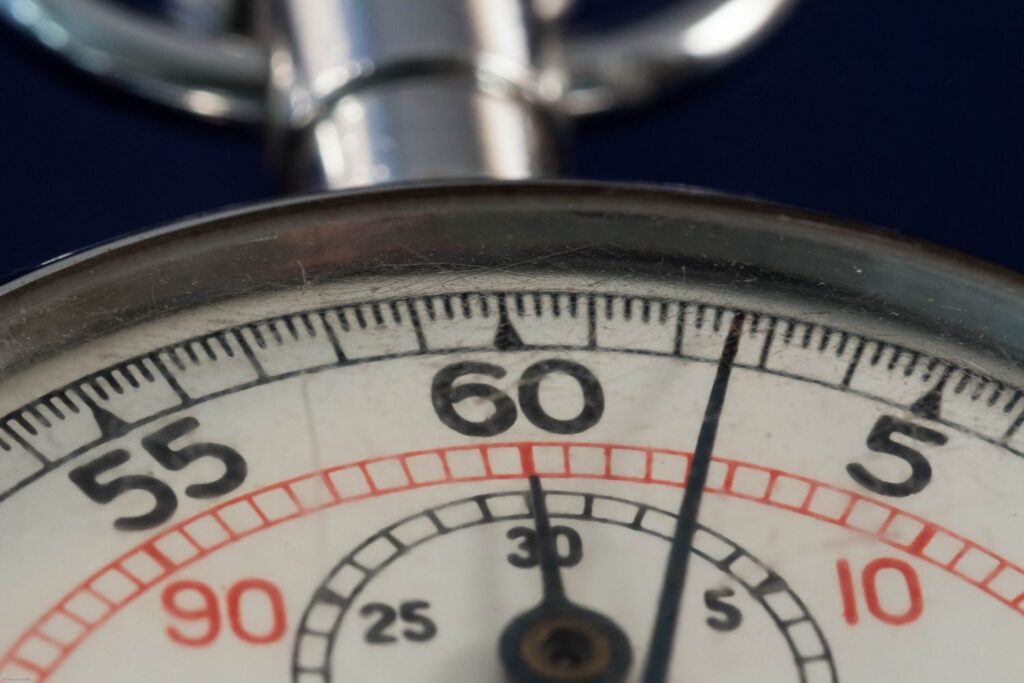

Have you ever stopped to ponder why there are 60 seconds in a minute and 60 minutes in an hour? It turns out that time, as we know it, is based on a system with a radix, or base, of 60. This might come as a surprise, as many of us are unaware of the mathematical underpinnings of our everyday lives.
Ancient Origins of Timekeeping
The roots of the base 60 system can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Sumerians and Babylonians. These cultures used a sexagesimal (base 60) numbering system for various measurements, including time. The choice of base 60 likely stemmed from the convenience of using our 10 fingers for counting. combined with the additional count from using the knuckles.
Evolution of the 60-Based Time System
The Babylonians further refined the concept of time by dividing the day into 24 hours, each hour into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds. This innovative approach to time measurement was revolutionary and laid the foundation for modern timekeeping.
Cultural Impact of Base 60
The adoption of the Sexagesimal for measuring time had a profound cultural impact. It influenced the development of mathematics, astronomy, and navigation. The sexagesimal system’s influence can be seen in the way we still measure time today, with 60 seconds in a minute and 60 minutes in an hour.
Practical Applications and Adaptations
The base 60 system has practical applications beyond timekeeping. It is used in various fields, including mathematics, astronomy, and geography. For example, astronomers use degrees (another base 60 unit) to measure angles in the sky. While navigators use degrees, minutes, and seconds to pinpoint locations on Earth’s surface.
The Surprising Legacy of Base 60
Despite its ancient origins, many people are unaware of the sexagesimal underlying our modern timekeeping. The ubiquity of this system in our daily lives is a testament to its enduring legacy and the innovative thinking of ancient civilizations.
Conclusion
Next time you glance at the clock and see 60 seconds ticking away in a minute. Remember that you’re witnessing the legacy of a mathematical system developed thousands of years ago. The base 60 system of time measurement is a fascinating example of how ancient cultures laid the groundwork for the concepts and systems we take for granted today.
Read Similar Posts…
- Read The Alpha’s Contract Ebook Free
- What Happens When You Ignore Hunger Cues?
- 7 Breakfast Foods You Need for Your Body Every Morning
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why do we use the base 60 for measuring time?
The exact origin is unclear, but some theories suggest that the Babylonians, who lived in Mesopotamia around 2000 BC, might have adopted a sexagesimal system (base 60) based on their astronomical observations and counting practices. They divided the day into 60 parts (called ush) and further divided each ush into smaller units. This system was later adopted by the Greeks and eventually influenced the way we tell time today.
- How is base 60 used in clocks?
We see the influence of base 60 in two ways:
Minutes and Seconds: There are 60 seconds in a minute and 60 minutes in an hour. This reflects the underlying sexagesimal system.
Circular Design of Clocks: Analog clocks have a circular face divided into 12 sections (hours). This might be a simplification of the original 60-unit system, making it easier to visualize and use in everyday life.
- Are there any advantages to using base 60 for time?
There are some arguments for and against using base 60:
Advantages: Base 60 allows for easy division of time into smaller units. 60 is divisible by many numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30), making it convenient to express fractions of an hour (e.g., 30 minutes, 15 minutes).
Disadvantages: Compared to a base 10 (decimal) system, base 60 can be considered less intuitive, especially for young children learning to tell time on analog clocks.
- Is base 60 still relevant in the digital age?
While digital clocks often display time in a decimal format (hours:minutes:seconds), the underlying concept of 60 seconds in a minute and 60 minutes in an hour remains the standard for most timekeeping systems. Even in digital time formats, seconds are further divided into milliseconds (thousandths of a second) and microseconds (millionths of a second), reflecting a continuation of the need for precise time measurement beyond whole numbers.
- Are there other cultures that used base 60 for timekeeping?
The Babylonians were not the only ones. The Maya civilization in Central America also employed a base-20 system for counting, which influenced their timekeeping practices, leading to some complexities in how they recorded dates and cycles.


